Smart home technology has rapidly evolved from a niche interest to a mainstream demand, offering unparalleled convenience, energy efficiency, and security. Among the many protocols available for smart home automation, KNX stands out as a leading standard. Recognized for its robustness, scalability, and interoperability, KNX provides a comprehensive solution for integrating various home automation systems into a unified and intelligent ecosystem.
This article explores the critical aspects of planning and designing a KNX-based smart home system. It covers everything from understanding the fundamental principles of KNX technology to the detailed steps involved in designing a customized smart home that meets the specific needs and preferences of its occupants.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is KNX?
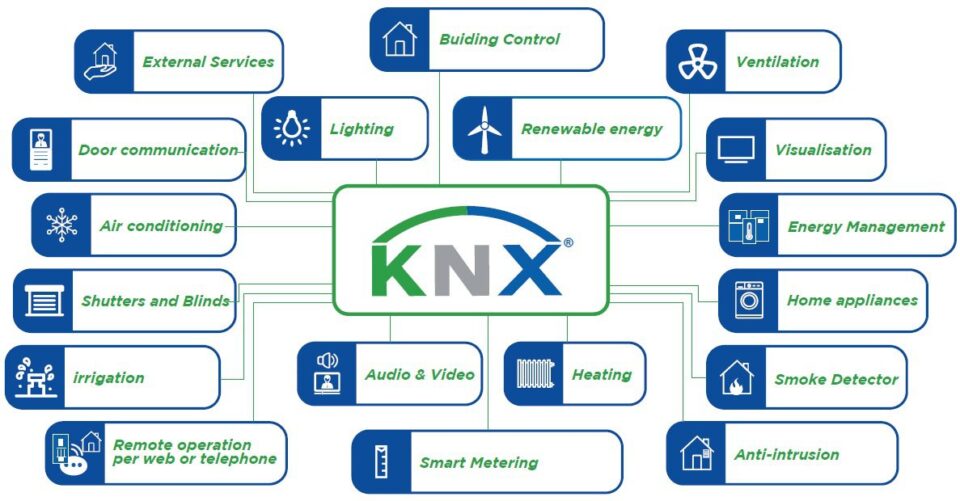
KNX is an open, standardized protocol for building automation, recognized by international standards (ISO/IEC 14543). It is used to control a wide range of devices, including lighting, heating, ventilation, security systems, and more. The protocol is designed to allow various devices to communicate with one another over a single bus network, enabling integrated control of a smart home.
Key Features of KNX
- Interoperability: KNX supports a wide range of devices from different manufacturers, ensuring that all components in a smart home system can work together seamlessly.
- Scalability: Whether for a single room or an entire building, KNX systems can be scaled to fit the size and complexity of the project.
- Flexibility: KNX systems can be easily reconfigured and expanded, allowing for future upgrades and additions without significant overhauls.
- Reliability: KNX is known for its stable and reliable performance, essential for critical home automation functions like security and climate control.
Components of a KNX System
- Sensors: These devices detect environmental changes (e.g., temperature, light, motion) and send signals to the control system.
- Actuators: Actuators receive commands from the control system and perform physical actions, such as adjusting lights or opening blinds.
- Controllers: The control units process inputs from sensors and user interfaces, sending commands to actuators to execute the desired actions.
- User Interfaces: These include touch panels, keypads, and mobile apps, allowing users to interact with the KNX system.
Planning a KNX-Based Smart Home System

Step 1: Needs Assessment
Before diving into the technical aspects of KNX system design, it is crucial to conduct a thorough needs assessment. This involves understanding the specific requirements of the homeowners and the functions they want to automate.
Key Questions to Consider:
- What are the primary goals?
- Are the homeowners looking to improve energy efficiency, enhance security, or increase convenience?
- Which areas of the home should be automated?
- Consider rooms like the living room, kitchen, bedrooms, and outdoor spaces.
- What devices and systems are currently in place?
- Assess existing electrical and mechanical systems to determine what can be integrated into the KNX system.
- What is the budget?
- The cost of a KNX system can vary widely based on the complexity and the number of devices. Establishing a budget will help guide the design process.
Step 2: System Layout and Design
Once the needs are clearly defined, the next step is to plan the layout of the KNX system. This involves mapping out where each device—sensor, actuator, controller, and interface—will be located within the home.
Design Considerations:
- Wiring Infrastructure:
- KNX systems typically use a dedicated twisted pair cable for communication, though wireless options are available. Planning the wiring routes is critical, especially for new constructions or major renovations.
- Zoning:
- Divide the home into zones, such as living areas, bedrooms, and outdoor spaces. Each zone can be controlled independently, allowing for more precise automation.
- Device Placement:
- Sensors should be placed where they can effectively monitor conditions, such as light sensors near windows or motion sensors in entryways. Actuators should be located close to the devices they control to minimize wiring complexity.
- Control Centers:
- Designate central locations for control panels or servers that will manage the KNX system. These should be easily accessible for maintenance and updates.
Step 3: Device Selection
Choosing the right devices is essential for ensuring that the KNX system meets the specific needs of the homeowners. The selection should be based on the functions required and the preferences of the users.
Key Devices to Consider:
- Lighting Control: KNX offers a wide range of options for lighting control, including dimmers, scene controllers, and color temperature adjustments. These devices can be programmed to create various lighting moods and enhance energy efficiency.
- Climate Control: Thermostats, heating actuators, and air conditioning controllers can be integrated into the KNX system to maintain optimal indoor conditions while minimizing energy consumption.
- Security Systems: KNX-compatible security devices include motion detectors, door and window contacts, surveillance cameras, and alarm systems. These can be linked to a central monitoring system for comprehensive home security.
- Shading and Blinds: Automated blinds and curtains can be controlled through KNX, responding to sunlight levels or time of day to improve comfort and reduce energy usage.
- Multimedia Integration: KNX systems can integrate with home entertainment systems, allowing users to control audio, video, and other media devices from a central interface.
Step 4: Programming and Configuration
Once the physical devices are installed, the KNX system needs to be programmed and configured. This process involves setting up the logic that dictates how the devices will interact with each other and how they will respond to user inputs.
ETS Software:
KNX systems are programmed using ETS (Engineering Tool Software), a specialized tool that allows installers to configure the communication paths and automation logic. ETS supports various programming tasks, from simple on/off commands to complex scenarios involving multiple devices and conditions.
Programming Steps:
- Define Communication Paths: Establish how devices will communicate within the KNX network. This includes linking sensors to actuators and setting up control commands.
- Set Up Logic Functions: Create logic functions that determine how the system will respond to different inputs. For example, a motion sensor might trigger the lights to turn on when someone enters a room.
- Test and Debug: After programming, thoroughly test the system to ensure all devices are functioning correctly. Debug any issues that arise to ensure reliable operation.
- User Customization: Provide options for users to customize settings, such as adjusting lighting scenes or setting temperature preferences. This can be done through user interfaces like touch panels or mobile apps.
Step 5: Installation and Commissioning
With the system programmed and configured, the next step is installation and commissioning. This involves physically installing the devices, connecting them to the KNX network, and ensuring that everything operates as expected.
Installation Tips:
- Follow Wiring Standards: Ensure that all wiring is done according to KNX standards and local electrical codes. Proper wiring is crucial for system stability and safety.
- Label Everything: Label all cables, devices, and control panels to make future maintenance and upgrades easier.
- Commissioning: Once the installation is complete, the system must be commissioned. This involves verifying that all devices are correctly installed, programmed, and communicating with each other. The commissioning process also includes documenting the system setup for future reference.
Step 6: User Training and Support
A successful KNX smart home system is not only well-designed and installed but also easy for the homeowners to use. Providing comprehensive user training and ongoing support is essential to ensure that the system meets the occupants’ needs.
User Training:
- System Overview: Provide an overview of how the KNX system works, including its main components and their functions.
- Using the Interface: Train users on how to interact with the system through touch panels, keypads, or mobile apps. This includes how to activate scenes, adjust settings, and troubleshoot basic issues.
- Customization: Show users how to customize settings to suit their preferences, such as creating personalized lighting scenes or setting temperature schedules.
Ongoing Support:
- Remote Monitoring: Offer remote monitoring and support services to assist with any issues that arise after installation. This can include software updates, troubleshooting, and system optimization.
- Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance visits to check the system’s performance, update software, and replace any faulty components.
- Upgrades: As new technology becomes available, provide options for system upgrades to ensure that the KNX system remains state-of-the-art.
Future-Proofing and Scalability

One of the major advantages of a KNX-based smart home system is its ability to adapt and grow with the needs of the homeowners. Planning for future expansion and ensuring that the system is scalable are crucial aspects of a successful KNX design.
Planning for Expansion
- Leave Room for Growth: Design the system with extra capacity in mind, such as additional wiring conduits or network ports, to accommodate future devices or features.
- Modular Design: Use a modular approach to design, where new zones or functions can be added without disrupting the existing system.
- Software Updates: Ensure that the system can be easily updated with new software or firmware to incorporate the latest features and security enhancements.
Sustainability Considerations
Incorporating sustainability into the design of a KNX-based smart home system is becoming increasingly important, not only for environmental reasons but also for cost savings over the long term. By optimizing energy use and integrating renewable energy sources, a KNX system can contribute significantly to a home’s sustainability.
Energy Efficiency:
- Automated Energy Management:
- KNX systems can automatically adjust heating, cooling, and lighting based on occupancy and environmental conditions, reducing energy waste.
- Energy Monitoring:
- Integrating energy meters within the KNX system allows homeowners to monitor real-time energy consumption and identify areas where efficiency can be improved.
- Smart Scheduling:
- Schedule devices like water heaters, washing machines, and dishwashers to run during off-peak hours when energy costs are lower.
Integration with Renewable Energy:
- Solar Power Integration:
- A KNX system can be integrated with solar panels to manage energy production and consumption, optimizing the use of solar energy for home automation tasks.
- Battery Storage:
- KNX systems can manage battery storage systems, ensuring that surplus energy generated by renewable sources is stored and used effectively.
- Electric Vehicle Charging:
- Smart scheduling of electric vehicle (EV) charging can be managed through KNX, taking advantage of lower energy rates and ensuring the vehicle is charged when energy demand is low.
Sustainable Materials:
- Eco-Friendly Components:
- When selecting devices and components, consider those made from sustainable materials or those with energy-efficient designs.
- Recyclable Systems:
- Plan for the future recycling of components, choosing devices that are easy to disassemble and recycle.
Impact on Home Value:
Investing in a KNX-based smart home system can increase the value of a property by making it more attractive to environmentally conscious buyers. Homes with advanced automation systems that promote sustainability are likely to stand out in the market.
Challenges and Considerations in KNX System Design
Designing and implementing a KNX-based smart home system is not without its challenges. Understanding these challenges and how to address them is essential for a successful project.
Technical Complexity
- Advanced Programming: KNX systems require sophisticated programming, often necessitating professional installers with specific training in KNX technology.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating KNX with other home automation protocols or legacy systems can be complex, requiring careful planning and testing.
- Troubleshooting: Diagnosing issues in a KNX system can be challenging due to the complexity of the network and the interdependence of devices.
Cost Considerations
- Initial Investment: The upfront cost of installing a KNX system can be higher than other home automation systems due to the need for specialized components and professional installation.
- Ongoing Costs: Consider the costs associated with maintaining, updating, and expanding the system over time.
User Experience
- Ease of Use: While KNX systems are highly customizable, they must be designed with the end-user in mind to ensure that the system is intuitive and easy to use.
- User Training: Providing adequate training is crucial to ensure that homeowners can take full advantage of the system’s capabilities.
Regulatory Compliance
- Electrical Standards: Ensure that the KNX system complies with local electrical codes and standards, which may vary by region.
- Data Privacy: With the rise of smart home technology, data privacy has become a significant concern. KNX systems should be designed with security features to protect user data and prevent unauthorized access.
Conclusion
Planning and designing a KNX-based smart home system is a multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of both technical and user-centric factors. From the initial needs assessment to the final commissioning and user training, each step is crucial to creating a system that is reliable, efficient, and tailored to the unique needs of the homeowners.
KNX stands out as a robust and flexible solution for smart home automation, offering unparalleled scalability and interoperability. By following a systematic approach to planning and design, it is possible to create a smart home that not only enhances comfort and convenience but also contributes to sustainability and energy efficiency.
As technology continues to evolve, KNX systems are well-positioned to integrate with new innovations, ensuring that your smart home remains at the forefront of automation technology. Whether you are planning a new construction or retrofitting an existing home, a well-designed KNX system can provide a future-proof solution that adapts to your changing needs and continues to deliver value for years to come.






