In today’s world, accessibility has become a crucial consideration in the design and construction of public and private buildings. Ensuring that all individuals, including those with disabilities, can access buildings safely and comfortably is a key priority. Automated door solutions play a significant role in achieving this goal by providing enhanced accessibility features that cater to a wide range of needs. This article explores the various types of automated door systems, their benefits, implementation strategies, and the impact they have on improving accessibility in both public and private buildings.
What Are Automated Door Solutions?
Automated doors are designed to open and close automatically, using sensors, timers, or remote controls. These systems are particularly beneficial in providing easy access to buildings for individuals with mobility challenges, such as those using wheelchairs, walkers, or crutches. Automated door solutions are also helpful for parents with strollers, people carrying heavy loads, and the elderly. They ensure that doors do not become barriers to entry, making buildings more inclusive and welcoming.
Types of Automated Door Systems
Automated door systems vary widely, each type catering to specific needs and environments. Understanding these options is essential for selecting the right system for a particular building.
- Automated Swing Doors: These doors operate by swinging open, either inward or outward. They are common in places where space is not an issue, such as main entrances or interior rooms. Automated swing doors can be fitted with sensors or push-button activations to accommodate individuals with mobility impairments.
- Automated Sliding Doors: Sliding doors are ideal for spaces where swing doors may not be practical due to space constraints. These doors open by sliding horizontally along a track, making them suitable for narrow corridors or high-traffic areas like malls and hospitals.
- Revolving Doors with Automation: Automated revolving doors control the flow of people while maintaining indoor climate conditions. These doors can be designed to adjust speed based on the user’s pace, offering accessible solutions in environments like airports and hotels.
- Folding Doors: Although less common, automated folding doors are used in areas where space is extremely limited. These doors fold in sections as they open, providing a wide entry in a small footprint, often seen in industrial settings.
- Low-Energy Doors: These are swing doors designed to open at a slower pace, reducing the risk of injury. Low-energy doors are particularly beneficial in environments like hospitals and nursing homes, where safety is a top concern.
Read more: How to Choose the Right Automatic Swing Gate Openers
Components of Door Automation
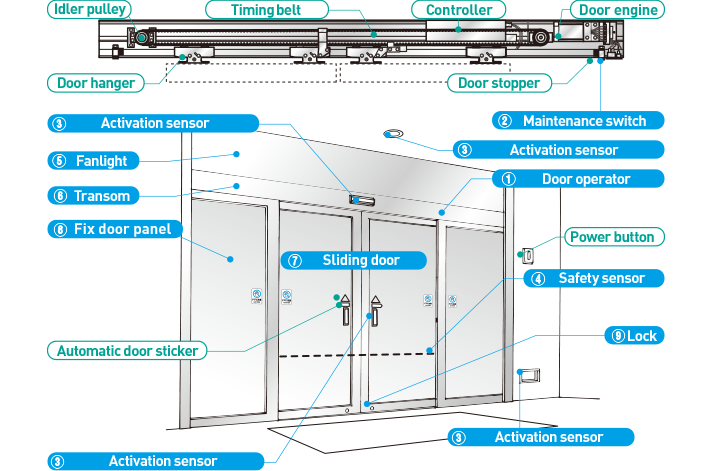
Door automation systems, especially for sliding doors, rely on several essential components to function smoothly and safely:
1. Activation Device
The activation device is responsible for detecting an “open” command and transmitting it to the control unit. These devices can be either manual or automatic. Manual activation devices include touchpads, remote controls, and buttons, while automatic devices use motion detectors, sensors, and photoelectric barriers. To ensure ease of use, multiple types of activation devices are often installed on the same automated door system.
2. Control Unit
The control unit serves as the central hub or “brain” of the door automation system. It manages the operational settings such as door opening speed, angle, and hold-open duration. The control unit may also integrate additional features like timer switches, access control systems, and video surveillance for enhanced security and functionality.
3. Drive Mechanism
The drive mechanism provides the motorized force required to open and close the door. It is the component that physically moves the door, pulling it open and pushing it closed as needed. This mechanism ensures the door operates smoothly and efficiently.
4. Sensor Strips
Sensor strips, also known as presence detectors, monitor the door’s movement path and the edges where it closes. They play a critical role in safety by stopping the door immediately if they detect a potential collision or entrapment of a person or object. Before installing these sensors, it’s important to verify their compatibility with any fire-rated doors in use.
These components work together to create a seamless and safe automated door system, enhancing accessibility, security, and convenience in both public and private buildings.
Read more: How Do Automated Sliding Gates Work?
Implementation Strategies for Automated Door Systems

Implementing automated door solutions requires careful planning and consideration of various factors to ensure that the system meets the needs of all users. The following strategies can help in the successful implementation of automated door systems:
- Assessment of User Needs: Before selecting and installing automated door systems, it’s important to assess the needs of the building’s users. This includes considering the types of disabilities or mobility challenges they may have, the volume of foot traffic, and any specific safety or security requirements.
- Compliance with Accessibility Standards: Automated door systems must comply with local accessibility standards and regulations. For example, in Australia, the Building Code of Australia (BCA) provides guidelines on the installation and operation of automated doors to ensure they are accessible to all individuals. These standards often dictate the width of door openings, the force required to open doors manually (if needed), and the height of control panels.
- Selection of Appropriate Door Types: The type of automated door selected should be based on the specific needs of the building and its users. For instance, sliding doors might be ideal for narrow entryways, while revolving doors may be better suited for high-traffic areas where energy efficiency is a concern.
- Integration with Building Design: Automated doors should be seamlessly integrated into the building’s design, both aesthetically and functionally. This includes ensuring that doorways are wide enough to accommodate automated systems and that the doors complement the overall architectural style of the building.
- Maintenance and Regular Testing: Like all mechanical systems, automated doors require regular maintenance to ensure they continue to operate smoothly and safely. Building owners and facility managers should establish a maintenance schedule that includes regular testing of sensors, control systems, and door mechanisms to identify and address any issues before they become serious problems.
- User Education and Signage: To maximize the benefits of automated door systems, building users should be educated on how to use them properly. Clear signage should be provided to indicate where automated doors are located and how to activate them, especially for individuals with visual impairments.
Read more: [2024] How Much Does Gate Automation Cost in Australia?
Benefits of Automated Door Solutions
Automated door solutions offer numerous benefits that enhance accessibility in public and private buildings:
- Improved Accessibility: Automated doors eliminate the need for physical effort to open or close doors, making buildings more accessible to individuals with disabilities, the elderly, and those with temporary injuries. This is particularly important in compliance with accessibility standards and regulations, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the United States and similar legislation worldwide.
- Increased Safety: Automated doors can be equipped with sensors that detect obstacles in their path, preventing accidents and injuries. For example, if someone is standing too close to a door, the sensor will prevent it from closing, reducing the risk of entrapment or collision.
- Energy Efficiency: Automated doors help maintain the internal temperature of buildings by reducing the amount of time doors remain open. This is especially true for revolving and sliding doors, which can minimize air exchange between the interior and exterior, leading to energy savings in heating and cooling.
- Enhanced Hygiene: In public buildings, automated doors reduce the need for physical contact with door handles, which can help prevent the spread of germs and bacteria. This is particularly important in healthcare facilities, food processing plants, and other environments where hygiene is critical.
- Convenience: Automated doors offer convenience to all building users, not just those with disabilities. Whether it’s a shopper with hands full of bags, a parent pushing a stroller, or an employee carrying equipment, automated doors provide a seamless and efficient entry experience.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications of Automated Door Solutions

The implementation of automated door solutions in public and private buildings has been widely adopted in various sectors, showcasing the tangible benefits of these systems.
- Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals and clinics have been among the early adopters of automated door systems due to the need for easy access and hygiene control. Automated sliding doors are commonly used in emergency rooms, operating theaters, and patient wards to provide quick and unobstructed access for patients and medical staff. Additionally, low-energy swing doors are often used in patient rooms to ensure safety and convenience.
- Retail and Commercial Buildings: Retail stores and shopping centers frequently use automated sliding and revolving doors to manage the flow of customers. These doors provide ease of access for shoppers carrying bags, pushing carts, or using mobility aids. In addition, automated doors help maintain indoor temperatures, contributing to energy efficiency in large commercial spaces.
- Educational Institutions: Schools, universities, and libraries use automated doors to accommodate students, staff, and visitors with varying mobility needs. Automated swing and sliding doors are commonly installed at main entrances, restrooms, and between different sections of buildings to ensure full accessibility.
- Transportation Hubs: Airports, train stations, and bus terminals are high-traffic environments where automated doors are essential for managing large volumes of passengers. Automated sliding and revolving doors are widely used in these settings to facilitate the smooth flow of people while maintaining security and energy efficiency.
-
Residential Buildings: In residential settings, automated doors are increasingly being used in multi-unit housing complexes and homes for the elderly or individuals with disabilities. Automated doors in these environments enhance independence by allowing residents to enter and exit their homes without assistance.
Conclusion
Automated door solutions are essential for enhancing accessibility in both public and private buildings. These systems not only comply with legal standards but also reflect a commitment to inclusivity, making buildings welcoming to all individuals, regardless of their physical abilities. The benefits of automated doors, including improved accessibility, safety, energy efficiency, and convenience, make them a vital component of modern building design. As technology advances, automated door systems will continue to evolve, offering even greater benefits and contributing to the creation of more inclusive environments.
Through careful planning, compliance with standards, and thoughtful integration, automated door solutions can significantly improve the quality of life for building users, ensuring that everyone has equal access to the spaces they need to live, work, and thrive.






