Lighting control systems have undergone a significant transformation in recent years, evolving from simple on/off switches to sophisticated, automated systems that offer enhanced comfort, energy efficiency, and integration capabilities. Among these advanced systems, KNX stands out as a leading open standard for commercial and residential building automation. This comprehensive guide explores the KNX lighting control system, covering its origins, key features, components, installation processes, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Origins and Evolution of KNX

KNX has its roots in the early 1990s, born from the convergence of three precursor technologies: the European Installation Bus (EIB), BatiBUS, and the European Home Systems (EHS). These technologies merged in 1999 to form the KNX Association, creating a unified and open standard for building automation. The primary goal was to establish interoperability and standardization, addressing the growing complexity and diversity of smart building solutions.
Since its inception, KNX has gained global recognition, supported by over 500 manufacturers and implemented in millions of buildings worldwide. The standard continues to evolve, incorporating new technologies and expanding its applications to meet the demands of modern building automation.
Key Features of KNX Lighting Control
KNX lighting control systems are distinguished by several key features that make them an attractive choice for building automation:
- Interoperability: KNX’s open standard ensures that devices from different manufacturers can communicate and work together seamlessly. This interoperability enables the creation of integrated and cohesive automation solutions.
- Scalability: KNX systems are highly scalable, suitable for small residential installations and large commercial projects. Users can start with a basic setup and expand it as needed without requiring significant reconfiguration.
- Flexibility: KNX supports various communication media, including twisted pair wiring, power line communication, radio frequency, and IP/Ethernet. This flexibility allows for diverse installation scenarios and easy integration with existing building infrastructures.
- Energy Efficiency: KNX systems provide precise control over lighting and other electrical systems, reducing energy consumption. Features such as automated dimming, daylight harvesting, and presence detection optimize energy use, contributing to sustainability efforts.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: KNX offers intuitive control interfaces, including wall-mounted switches, touch panels, and mobile apps. These interfaces make it easy for users to manage lighting settings and create customized scenes.
- Reliability and Security: KNX is known for its robust communication protocols, ensuring reliable data transmission and protecting against unauthorized access. This reliability is crucial for critical applications in both residential and commercial settings.
Read more: Why Choose KNX for Commercial Building Automation?
Components of a KNX Lighting Control System
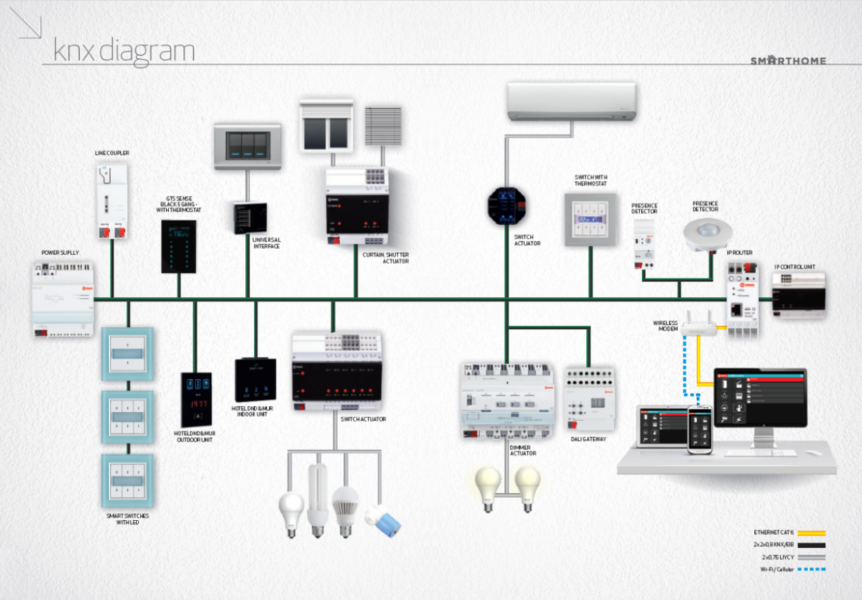
A typical KNX lighting control system consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in its operation:
- Sensors: Sensors detect changes in the environment, such as motion, light levels, and occupancy. Common types include presence detectors, daylight sensors, and temperature sensors. These devices provide real-time data that the system uses to adjust lighting accordingly.
- Actuators: Actuators control the lighting devices based on commands received from the system. They can switch lights on or off, dim them, or change their color. Examples include relay modules, dimmer actuators, and RGB controllers.
- Controllers: Controllers are the brains of the system, processing inputs from sensors and user interfaces to send appropriate commands to actuators. They can be centralized or distributed throughout the building.
- User Interfaces: These are the points of interaction for users, allowing them to control the lighting system. They include wall switches, touch panels, remote controls, and smartphone apps.
- Communication Backbone: The KNX communication backbone can use various media, such as twisted pair cables (KNX TP), power lines (KNX PL), radio frequency (KNX RF), and IP networks (KNX IP). This backbone ensures effective communication between all system components.
Installation and Configuration
Installing and configuring a KNX lighting control system involves several steps:
- Planning: The first step is to plan the system layout, considering the building’s requirements, the number of devices, and their locations. This stage involves designing the communication infrastructure and selecting appropriate components.
- Wiring: For wired systems, installation includes running cables to connect sensors, actuators, controllers, and user interfaces. The KNX TP (twisted pair) wiring is commonly used for its reliability and ease of installation.
- Programming: Once the hardware is in place, the system needs to be programmed. This involves configuring devices, setting up communication parameters, and creating automation logic. KNX systems are typically programmed using specialized software tools provided by manufacturers.
- Testing and Commissioning: After programming, the system must be thoroughly tested to ensure all components work as expected. This phase includes verifying sensor responses, actuator actions, and user interface functionality.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Regular maintenance is essential to keep the system running smoothly. This includes updating software, checking connections, and replacing faulty components. The open standard of KNX makes it easy to upgrade the system with new devices and features over time.
Benefits of KNX Lighting Control
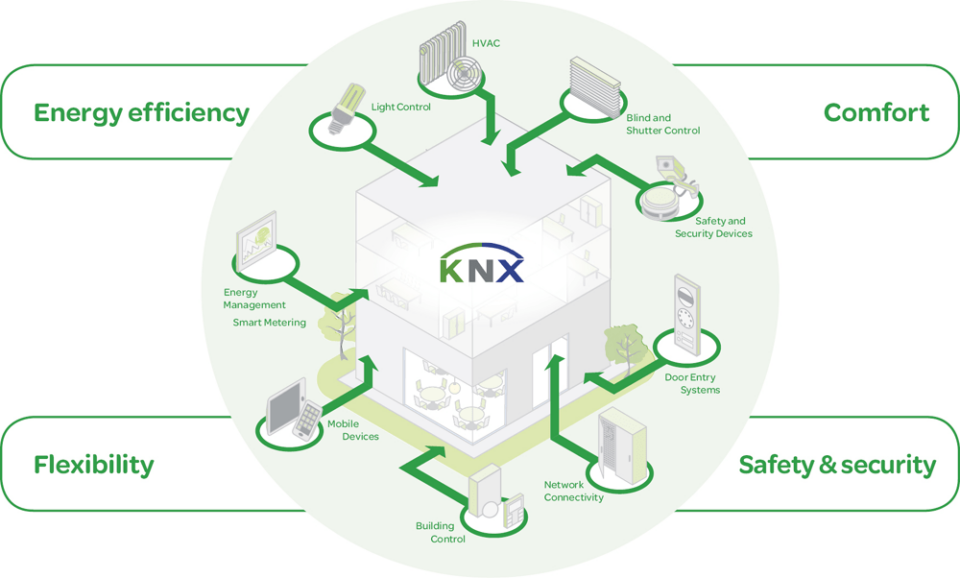
The adoption of KNX lighting control systems brings numerous benefits, making them a compelling choice for modern building automation:
- Enhanced Comfort and Convenience: KNX allows users to create personalized lighting scenes that suit their preferences and activities. A single button press can adjust lighting for different scenarios, such as a cozy movie night or a focused work environment.
- Increased Energy Savings: KNX’s ability to automate lighting based on occupancy and natural light levels significantly reduces energy wastage. This not only lowers utility bills but also contributes to environmental sustainability.
- Future-Proofing: The open nature of the KNX standard ensures that systems can adapt to new technologies and requirements over time. This future-proofing protects the investment and allows for continuous upgrades without starting from scratch.
- Improved Building Value: Buildings equipped with advanced KNX automation systems are often more attractive to buyers and tenants. The added convenience, efficiency, and modernity can enhance property value and marketability.
- Integration with Other Systems: KNX lighting control is not limited to just lighting. It can be integrated with HVAC systems, security, shading, and more, providing a comprehensive automation solution that enhances overall building performance.
Applications of KNX Lighting Control

The versatility of KNX lighting control makes it suitable for a wide range of applications:
- Residential Buildings: In homes, KNX can control not only lighting but also heating, cooling, and security systems. Homeowners can enjoy personalized comfort settings, enhanced security, and energy savings.
- Commercial Buildings: Office buildings, retail spaces, and hotels benefit from KNX’s ability to create optimal lighting environments. For example, in an office, KNX can adjust lighting based on occupancy and daylight, promoting a productive and comfortable workspace.
- Public Buildings: Museums, airports, and schools can utilize KNX for efficient lighting management. Automated lighting schedules, presence detection, and centralized control contribute to operational efficiency and user comfort.
- Industrial Facilities: In factories and warehouses, KNX can help optimize lighting for safety and efficiency. Integrating with other automation systems, KNX ensures that lighting supports the overall productivity and operational requirements of the facility.
Challenges and Considerations
While KNX lighting control offers numerous advantages, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Initial Cost: The initial cost of installing a KNX system can be higher than conventional lighting systems. However, the long-term energy savings and increased building value often justify the investment.
- Complexity: Designing, installing, and programming a KNX system requires specialized knowledge and skills. It is crucial to work with experienced professionals to ensure a successful implementation.
- Compatibility: Although KNX is an open standard, not all devices are guaranteed to be compatible. It is important to choose certified KNX products and verify their interoperability before installation.
- Security: As with any networked system, security is a critical concern. Proper encryption, authentication, and access control measures must be implemented to protect the system from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Future Trends in KNX Lighting Control
The future of KNX lighting control looks promising, with several emerging trends and developments:
- Integration with IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) is driving greater connectivity and intelligence in building automation. KNX systems are increasingly integrating with IoT platforms, enabling advanced data analytics, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance.
- Wireless Solutions: While wired KNX systems are well-established, wireless KNX solutions are gaining popularity for their ease of installation and flexibility. KNX RF and KNX IP are key technologies enabling wireless communication in KNX systems.
- Energy Harvesting: Energy harvesting technologies, such as solar-powered sensors and switches, are being integrated into KNX systems. These devices can operate without external power sources, reducing installation costs and improving sustainability.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning are being applied to KNX systems to enhance automation capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze sensor data and user behavior to optimize lighting settings and predict maintenance needs.
- Enhanced User Interfaces: The development of more intuitive and interactive user interfaces, including voice control and augmented reality, is making KNX systems more accessible and user-friendly.
Conclusion
KNX lighting control systems are revolutionizing building automation, offering unparalleled flexibility, efficiency, and integration capabilities. As an open standard, KNX enables seamless communication between devices from different manufacturers, ensuring a cohesive and future-proof solution. With its numerous benefits, including energy savings, enhanced comfort, and increased building value, KNX is set to remain a cornerstone of smart building technology. As the industry continues to evolve, emerging trends such as IoT integration, wireless solutions, and AI applications will further enhance the capabilities and appeal of KNX lighting control systems.
This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for understanding KNX lighting control systems, highlighting their key features, benefits, and applications. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial use, KNX offers a robust and adaptable solution for modern lighting control needs.






